Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate, which is quite common today.
The prostate gland is a male organ, and therefore the disease is entirely male.
Why is a prostate needed? The prostate gland is responsible for the following functions:
- creates a liquid portion of sperm with the bladder neck muscles;
- creates an internal sphincter;
- forms testosterone to dihydrotestosterone.
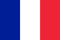
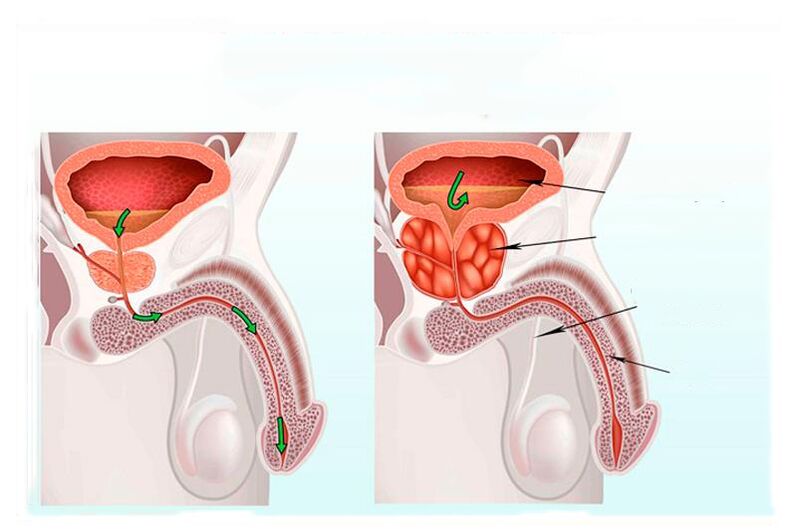
The prostate gland or simply the prostate is located below the bladder, the urethra passes through the prostate and therefore the prostate is located around the urethra. And because the prostate enlarges during inflammation, it compresses the urethra and makes it difficult to urinate. Men over the age of forty very often suffer from prostatitis, it is the result of a malfunction of the genitourinary system.
Factors that provoke the development of prostatitis:
- hypothermia;
- infectious diseases;
- alcohol and tobacco use;
- trauma and hormonal disorders;
- sedentary work;
- urinary retention.
Prostatitis is divided into several types:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis: occurs during damage to prostate tissue Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, etc.
- Many of these bacteria are representatives of healthy microflora and live on our skin and stomach, but entering the prostate tissue they cause inflammation. The main symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are nausea and pain in the groin and lower back, frequent going to the toilet and pain during urination, intoxication of the body and reduced quality of erection, signs of blood in the urine.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis: occurs due to injuries of the genitourinary system or the presence of infections in the organs.
- Symptoms of chronic prostatitis are manifested as pain during urination and frequent urge, discomfort in the groin, the presence of blood in the semen, a rise in body temperature by 0, 5 - 1 degree Celsius.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis occurs due to lifting heavy objects with a full bladder, as a result, urine enters the prostate, pelvic floor muscle spasms, therefore - increased pressure in the prostate, injuries. Symptoms include pain when urinating, and only laboratory tests can detect a contagious difference.
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is a dangerous disease that, unlike prostatitis, carries with it a bunch of vague questions. What is chronic prostatitis? Chronic prostatitis is the presence of inflammation in the prostate, which is characterized by numerous changes in the tissues and functional disorders of the prostate, the activity of the male reproductive system. Chronic prostatitis is among the first diseases of the male reproductive system. The classification of chronic prostatitis is divided into several subtypes:
- acute bacterial prostatitis;
- chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- chronic abacterial prostatitis;
- inflammatory prostatitis with increased leukocytes in prostate secretion;
- non-inflammatory process without increase in leukocytes;
- asymptomatic prostate inflammation, which is detected randomly.
Infection caused by neurovegetative disorders causes and provokes the development of chronic prostatitis. Hemodynamic disorders cause a decrease in immunity through autoimmune and biochemical processes. Factors in the development of chronic prostatitis are lifestyle features that cause infection of the genitourinary system, frequent hypothermia and inactive work, irregular sex life or the constant presence of a urethral catheter. Also important and dangerous causes of the disease will be disorders of the immune system, cytokines, bacteria of low molecular weight polypeptide nature, which affect the functional activity of immune cells.
One of the main reasons for the development of non-inflammatory forms of chronic prostatitis is pelvic floor dysfunction.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
Signs of chronic prostatitis are pain and discomfort, urinary dysfunction and sexual dysfunction. The presence of pain in the pelvic region, perineum and groin. Pain is often seen in the anus and scrotum. Sex life is disturbed and libido is also reduced, but these signs are not noticed in all patients. Chronic prostatitis is interchangeable in nature, the symptoms worsen and then subside. In general, the symptoms of chronic prostatitis are similar to the stages of the inflammatory process. Pain in the scrotum and groin is characteristic of the exudation stage, as is frequent urination, accelerated ejaculation, and painful erections. The alternative phase is characterized by pain in the suprapubic part, normal urination, and with accelerated eruption of semen, pain during erection is not noticed. In the proliferation phase, we can also see increased urination, and the ejaculation process is slightly delayed. In the stage of prostate sclerosis, in addition to cicatricial changes, the patient also has pain in the suprapubic part, frequent urination, and ejaculation of semen is slow or completely absent. It should also be borne in mind that the phases and disorders described above do not always appear in everyone.
Numerous tests and laboratory tests will help to diagnose chronic prostatitis, since the disease is very often asymptomatic. Testing is also important to help the doctor recognize the intensity of symptoms, pain and urination disorders. Laboratoryexamination of chronic prostatitis helps in diagnosing chronic prostatitis and possible infection of the prostate with atypical bacterial and fungal flora and viruses. If there are no bacterial growths in the secretions of the prostate with an increased number of leukocytes, chlamydia should be analyzed. Microscopic examination helps to detect the number of leukocytes and mucus, trichomonads and epithelium in the secretion of the urethra. The secret obtained by prostate massage is taken for a bacteriological examination, and according to its results, the nature of the disease is determined. It is also important to conduct an immunological study whose results help to determine the stage of the disease and monitor the effect of treatment. An instrumental study of chronic prostatitis helps to determine the stage and form of the disease by further observation throughout treatment. Ultrasound examination can study the size and volume of the prostate, the structure of the cyst and sclerotic changes in the organ, the degree of expansion and the density of the contents of the seminal vesicles. Myography of the muscles and bottom of the pelvis plus information on suspected neurogenic urinary disorders. An X-ray study is performed to clarify the cause and course of further treatment of chronic prostatitis. Computed tomography of the pelvic organs is performed in order to exclude pathological changes in the spine and pelvic organs. Diagnosis as a way to exclude a disease that is inappropriate for symptoms helps to determine the nature of the pathological process: with inflamed processes in other organs; with diseases of the rectum; with sexual dysfunctions; with neuropsychiatric disorders, for example, depression or reflex sympathetic dystrophy.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis must be consistent and comprehensive. First, it is necessary to change the usual way of life and thinking of the patient. Also remove the influence of harmful factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption, hypothermia. Thus, we stop the further development of the disease and soon cause recovery. Even in the preparatory phase for treatment, adherence to a diet and the establishment of sexual life play an important role. The next major course in the treatment of the disease is the use of drugs. Such a correct approach to the treatment of chronic prostatitis will help not only to fight the disease, but also to increase the effectiveness of treatment at each stage of the development of prostatitis. Chronic prostatitis generally does not require hospitalization, but in severe cases of chronic prostatitis, hospital treatment is more useful and effective than outpatient treatment. Drug treatment leads to the establishment of good blood circulation in the pelvic organs, brings hormones and the immune system to a normal level. In such cases, antibacterial drugs and immunomodulators, vasodilators and prostate massage are used. Antibacterial use of drugs is the basis for the treatment of chronic prostatitis. But, unfortunately, the effectiveness of this therapy has been proven, but not for all types of prostatitis. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, antibacterial treatment is effective, in chronic abacterial prostatitis, a course of empirical antibacterial treatment is used.
Currently, local physical treatment is very important. Laser, mud and electrophoresis physiotherapy is considered the most effective. Electromagnetic radiation is based on anticongestive and bacteriostatic action. Low-energy laser therapy stimulates microcirculation in prostate tissues, and laser therapy also has a biostimulating effect. In the absence of contraindications, therapeutic prostate massages are used.
Surgical intervention is increasingly used in the treatment of prostatitis as the disease affects more and more young men. An indication for surgery may be sclerosis of the seminal tubercle; such patients often consult a physician with signs of lack of sexual sensation and ejaculation. In such cases, resection of the seminal tubercle is performed. Also, surgery is used for sclerosis of the bladder and prostate.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Often men suffering from prostatitis complain of fever and fever, even if the temperature measured under the arm is normal, then very often the temperature in the anus will be elevated. Pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, perineum, anus and scrotum also serve as a signal to go to the doctor. Even more frequent urination, cramps and a burning sensation when urinating. There is a worsening of the general condition, weakness, pain in the muscles and bones, severe headaches.
With inflammation of the prostate in men, urination is difficult, which is often accompanied by urinary retention. Constipation that occurs due to compression of the rectum by an enlarged gland is characteristic of the disease.
Treatment of prostatitis
Before starting treatment, you must be sure of the diagnosis. The minimal manipulations that should be performed are measurement of the temperature in the anus, diagnosis and palpation of the inguinal perineum of the lymph nodes, general clinical blood test and general urine test. You will also need to take urethral swabs and bacterioscopy of urine and sediment. In addition, a transrectal prostate ultrasound is performed.
The temperature in the anus is usually increased and differs from the temperature of the mouse mode by about one degree. In the analysis of urine, the indicator of the number of leukocytes was exceeded. Some changes are also noted in blood tests, for example, the number of eosinophils decreases and neutrophilic leukocytosis occurs. In immunosuppressed patients, sepsis is often seen with complications of prostatitis.
By palpation of the perineum the patient feels pain, the patient has an increase in inguinal lymph nodes. The prostate gland is enlarged during palpation, swollen and hot to the touch, and sometimes with heterogeneous inflammatory seals. If the prostate is inflamed, a biopsy is not performed and the infection can spread further.
Treatment of prostatitis consists in the use of antibiotics against the microorganisms that cause this disease. Antipyretic drugs are also prescribed to lower body temperature and use emollient laxatives to facilitate bowel emptying. The patient is prescribed a course of massage which consists of squeezing the inflamed secretion with the fingers, squeezing it into the canals and finally into the urethra. Prostate massage improves blood circulation and has a good effect on prostate muscle tone.
Prevention of prostatitis
First of all, to prevent prostatitis, you should limit yourself to food and apply a special diet. You need to include foods like parsley, asparagus, strawberries in your diet, and if you like pasta and so on, these should be hard varieties. You should also rule out bad habits and alcohol, spicy foods. With the worsening of the disease, it is very important to exclude sex life.
To prevent prostatitis, it is necessary to exclude all risk factors for its occurrence, which are: pay attention to proper nutrition, exclude bad habits and lead a regular sexual life, because it does not allow the accumulation of sperm. Every young guy should know that promiscuity in sexual intercourse is harmful to the prostate. An active sex life increases the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases. In any case, use contraception. Monitor your bowels and go to the toilet regularly. Another important thing is work: if it is connected to a sedentary way, then you need physical activity, running, swimming and tennis will also come in handy. Also, do not forget about daily walks in the fresh air, it is very useful for the whole body. Hypothermia negatively affects the immune system and at this point the infection progresses. You should see a urologist, even if there are no prerequisites for it.
Timely treatment of any urogenital infection will help eliminate the cause of the development of prostatitis.
Folk remedies for the prevention of prostatitis are also popular, on the basis of which recipes such as inclusion in the diet of honey, nuts and dried fruits, rich in vitamins and minerals, differ. Pumpkin and onion seeds, oatmeal and seafood, liver and apples are rich in zinc and therefore have a special, important value and great benefits for the prostate. Add to the above tips: empty your stomach completely and avoid constipation. This will help products like kefir, vegetable oil and vegetable fiber. The benefits of exercises for the intimate muscles should also be mentioned separately.
Exercises for the prevention of prostatitis are simple and do not require special adaptation, they can be performed at any time and anywhere. Here are a few examples: perform perineal movements as if pulling in the rectum; tense the muscles of the perineum, trying to stop urination, keep them in this position as long as possible; while lying down, lift your pelvis and hold it for twenty or thirty seconds, repeat these movements until you feel pain and fatigue in your buttocks. Such simple exercises will only be a plus for your body.